IMPLANTOLOGY BY INTRAORAL WELDING
The main advantage
The main advantage of implants is that the teeth have exactly the same structure and function as natural teeth, restoring the appearance and function of the mouth.
Immediate-load IMPLANTOLOGY procedures using INTRAORAL WELDING can be carried out with both abutments and two-stage implants. Because the titanium bar is syncrystallised, immediate loading is possible. After 4 months the bar is removed for cosmetic and prosthetic reasons.





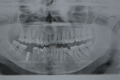 Zirconia crown on two-stage implant images gallery.
Zirconia crown on two-stage implant images gallery. 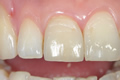 Lithium disilicate veneers images gallery.
Lithium disilicate veneers images gallery. 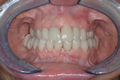 Lithium disilicate fixed dentures images gallery
Lithium disilicate fixed dentures images gallery 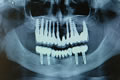 Orbital composite fixed dentures on abutment implants images gallery
Orbital composite fixed dentures on abutment implants images gallery
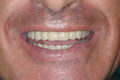 Composite fixed dentures on abutment implants images gallery
Composite fixed dentures on abutment implants images gallery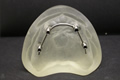 Fixed arch on 4 implants images gallery
Fixed arch on 4 implants images gallery 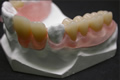 Removable or skeletal dentures images gallery
Removable or skeletal dentures images gallery